Jute and Jute-Diversified Products of Bangladesh: A Sustainable Future
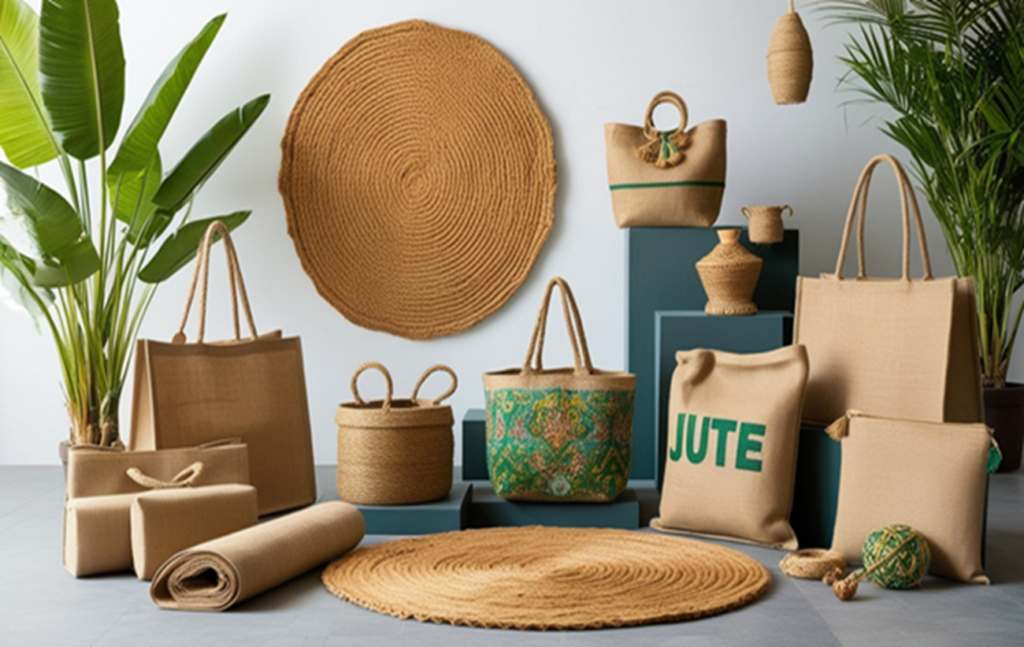

Bangladesh, known as the “Golden Fiber Land,” is one of the world’s largest producers and exporters of jute and jute-diversified products. Jute, a natural fiber with remarkable versatility, is deeply rooted in Bangladesh’s culture and economy. In recent years, the demand for eco-friendly alternatives has surged, making jute and its diversified products a key player in the global sustainable movement.
Bangladesh’s jute export sector is Bangladesh’s proud claim to sustainability both in terms of natural fibers and in the number of livelihoods supported in the value chain. Bangladesh is the world’s second largest producer of jute, the world’s largest exporter of jute and jute products, as well as the origin of the finest quality of jute. The North Eastern part of Bangladesh is a jute-growing area that is popular for having the highest quality of jute fiber, which can be claimed to be one of the best qualities of jute in the world. The sector has, however, not fully been able to maximize the potential that crop offers as it falls somewhat behind her other competitors in applying recent technological advancements. Catching up on this front would unleash the sector’s true potential.
Bangladesh Exports of Jute & Jute goods (US$ million)
| Products | 2016-17 | 2017-18 | 2018-19 | 2019-20 | 2020-21 | 2021-22 |
| Jute & Jute goods | 962.42 | 1025.55 | 816.27 | 882.35 | 1161.48 | 1127.63 |
| Raw Jute (5303) | 167.84 | 155.68 | 112.48 | 129.89 | 138.15 | 216.18 |
| Jute Yarn & Twine (5307) | 607.88 | 647.72 | 512.42 | 564.26 | 799.04 | 697.80 |
| Jute Sacks & Bags (630510) | 127.53 | 122.82 | 82.86 | 106.54 | 138.66 | 119.23 |
| Others | 59.17 | 99.33 | 108.51 | 81.66 | 85.63 | 94.42 |
Source: EPB Data
Jute product exports have shown consistent growth over recent years. The sector has also continued to diversify, thanks to various
initiatives to widen the range. This is also to thanks to the unique qualities of golden fiber and advances in methods of blending that
enable the creation of less crude products.
Bangladesh is producing a widening range of jute products including close to 300 Jut Diversified Products (JDP). Notable categories
of JDPs include home textiles, household furniture, decoration, gardening items, paper/packaging products, office stationery, floor
cover/mat, bags, jute geo-textile, fashion accessories and footwear.
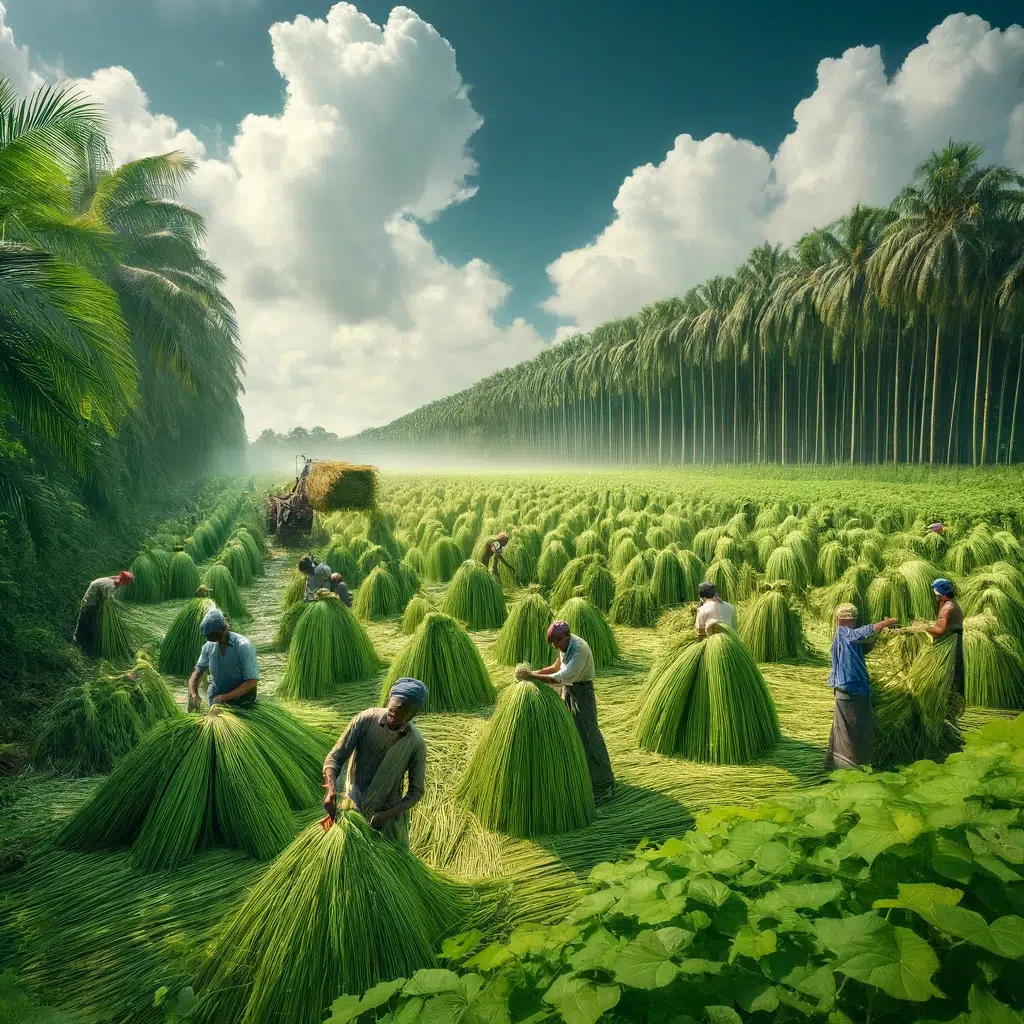

Images: A lush green jute field in Bangladesh with farmers harvesting jute.
The Legacy of Jute in Bangladesh:
Jute has been cultivated in Bangladesh for centuries and remains a major agricultural and industrial sector. It provides livelihoods for
millions of farmers and workers in processing, manufacturing, and exporting jute-based goods. The unique climate and fertile soil
of Bangladesh contribute to producing high-quality jute fibers, making the country a dominant force in the global jute industry
Jute is a vital part of Bangladesh’s culture, economy, and history. It’s been called the “golden fiber” of Bangladesh.
History:
- Jute has been a part of Bengal culture for centuries.
- During the British Governance, jute was exported to the United Kingdom for processing.
- Jute was a major export item and one of the country’s largest industries.
- The jute industry declined in the 1970s due to the rise of synthetic fibers.
Current status:
- Bangladesh is the second-largest producer of jute in the world.
- Bangladesh is a leader in jute exports.
- Jute is still a vital sector of Bangladesh’s economy.
- Jute products are environmentally friendly.
- Bangladesh earns foreign currency by exporting jute and jute products.
Future of jute :
- Bangladesh is committed to maintaining its legacy while innovating for the future.
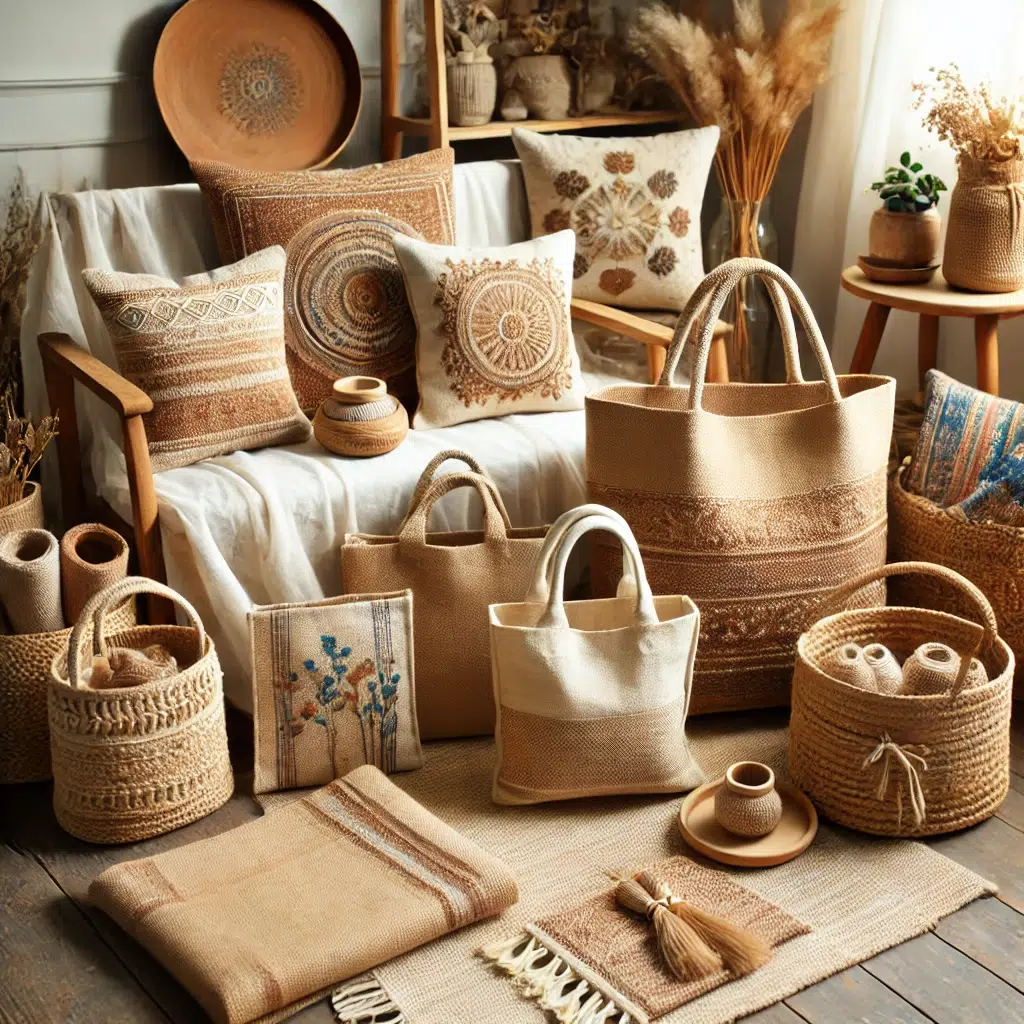

Images: A beautiful display of jute bags and home decor items.
Jute-Diversified Products: Innovation and Sustainability:
Traditionally, jute was used for making sacks, ropes, and carpets. However, with the advancement of technology and
innovative craftsmanship and jute-diversified products have gained popularity across multiple industries. Some of the
most sought-after jute-based products include:
- Jute Bags – Stylish, durable, and biodegradable, jute bags are widely used as shopping, tote, and promotional bags.
- Jute Home Decor – Jute rugs, curtains, table mats, and cushion covers bring an organic and aesthetic touch to modern interiors.
- Jute Furnishings – Eco-conscious consumers prefer jute furniture, wall hangings, and decorative pieces.
- Jute-Based Apparel – Sustainable fashion brands use jute fabric to create trendy and eco-friendly clothing.
- Jute Paper and Stationery – Jute pulp is used to manufacture handmade paper, notebooks, and eco-friendly packaging.
- Jute Composite Products – Jute fiber is used in making eco-friendly automotive parts, geotextiles, and biodegradable plastics.
Environmental Benefits of Jute:
Jute is one of the most environmentally friendly fibers in the world. Some key ecological benefits include:
- Biodegradable & Compostable – Jute decomposes naturally, reducing environmental pollution.
- Carbon Absorption – Jute plants absorb large amounts of CO2 and release oxygen at a higher rate than trees.
- Low Water & Pesticide Usage – Unlike cotton, jute requires minimal water and fewer pesticides, making it a sustainable crop.
- Soil Enrichment – Jute cultivation improves soil fertility, benefiting crop rotation.
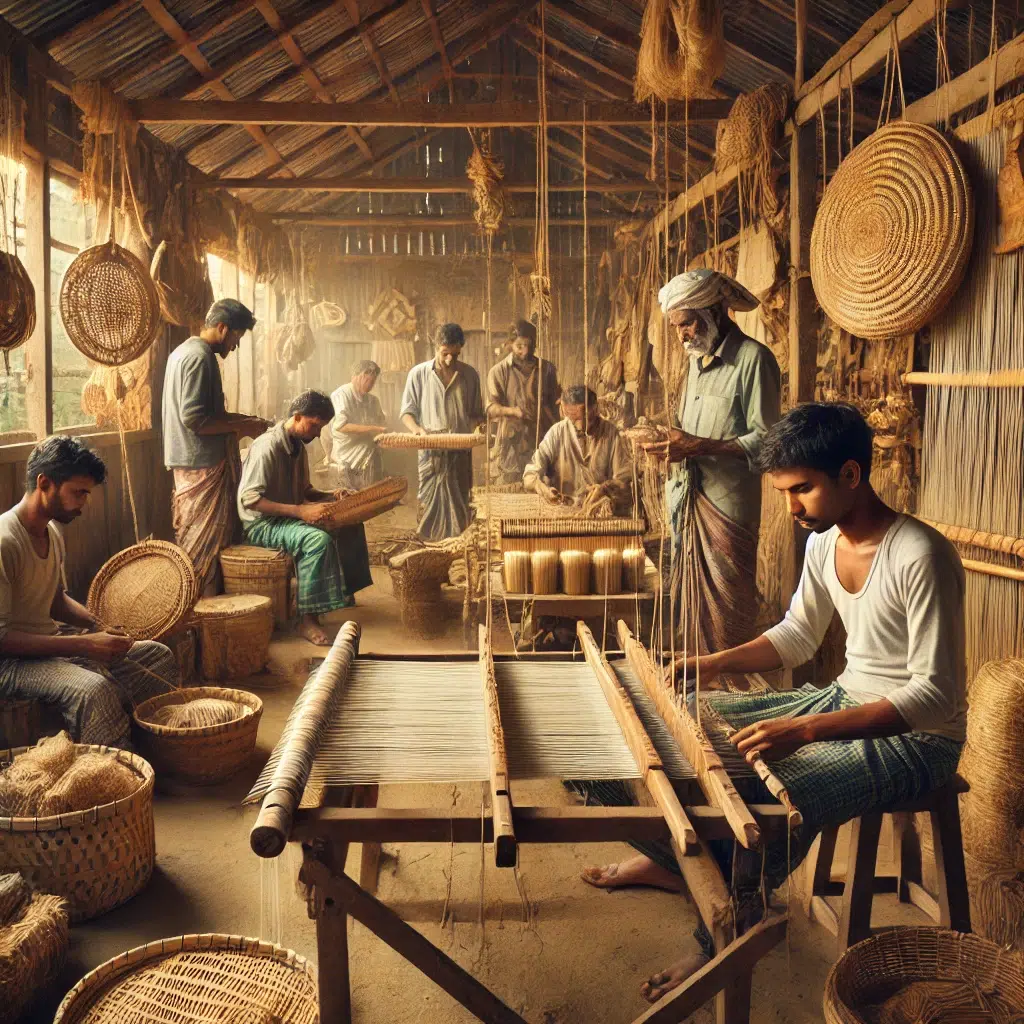

Images: Bangladeshi artisans weaving jute-based products in a traditional workshop.
Bangladesh’s Position in the Global Jute Market:
Bangladesh exports jute and jute-diversified products to more than 100 countries. Europe, North America, and the Middle East are
major markets for Bangladeshi jute goods. Government policies and private sector initiatives are boosting jute product innovation
and increasing market access.
The Future of the Jute Industry in Bangladesh:
As the world shifts toward eco-friendly solutions, jute holds immense potential for Bangladesh’s economy. Sustainable
branding, technological advancements, and international collaborations will help elevate the industry to new heights.
Moreover, initiatives to promote jute-based products in domestic and global markets will strengthen Bangladesh’s position
as a leader in green alternatives.
Conclusion:
Jute and jute-diversified products are more than just an industry in Bangladesh—they represent a commitment to sustainability
and a greener future. By embracing innovation and expanding market reach, Bangladesh continues to uphold its legacy as a
leading producer of jute, paving the way for an environmentally responsible world.

Explore Jute with EdconAura:
At EdconAura, we believe in sustainable sourcing and promoting eco-friendly products. Whether you’re looking for high-quality
jute decor, bags, or furnishings, our curated collection showcases the best of Bangladesh’s craftsmanship. Keep in touch with
us to learn more about our upcoming jute product offerings!